
The world around us is undergoing a fascinating transformation and how! Everyday objects and devices are communicating with each other to enhance our lives. We can control our coffee machines, thermostats, lights, and security systems remotely. Our cars have become smarter, with GPS systems and connected features enhancing our driving experience. Healthcare is positively impacted with advent of wearable devices and thus paving the path for healthier world. What an exciting time to be alive!
This is the phenomenon called IoT — a system where the internet is connected to the physical world via ubiquitous sensors, as per Kevin Ashton
IoT is a human-centered revolution empowering us to make informed decisions, and shape a future intertwined with technology. It revolutionizes the way we approach and engage with our surroundings, offering unprecedented opportunities for growth and advancement.
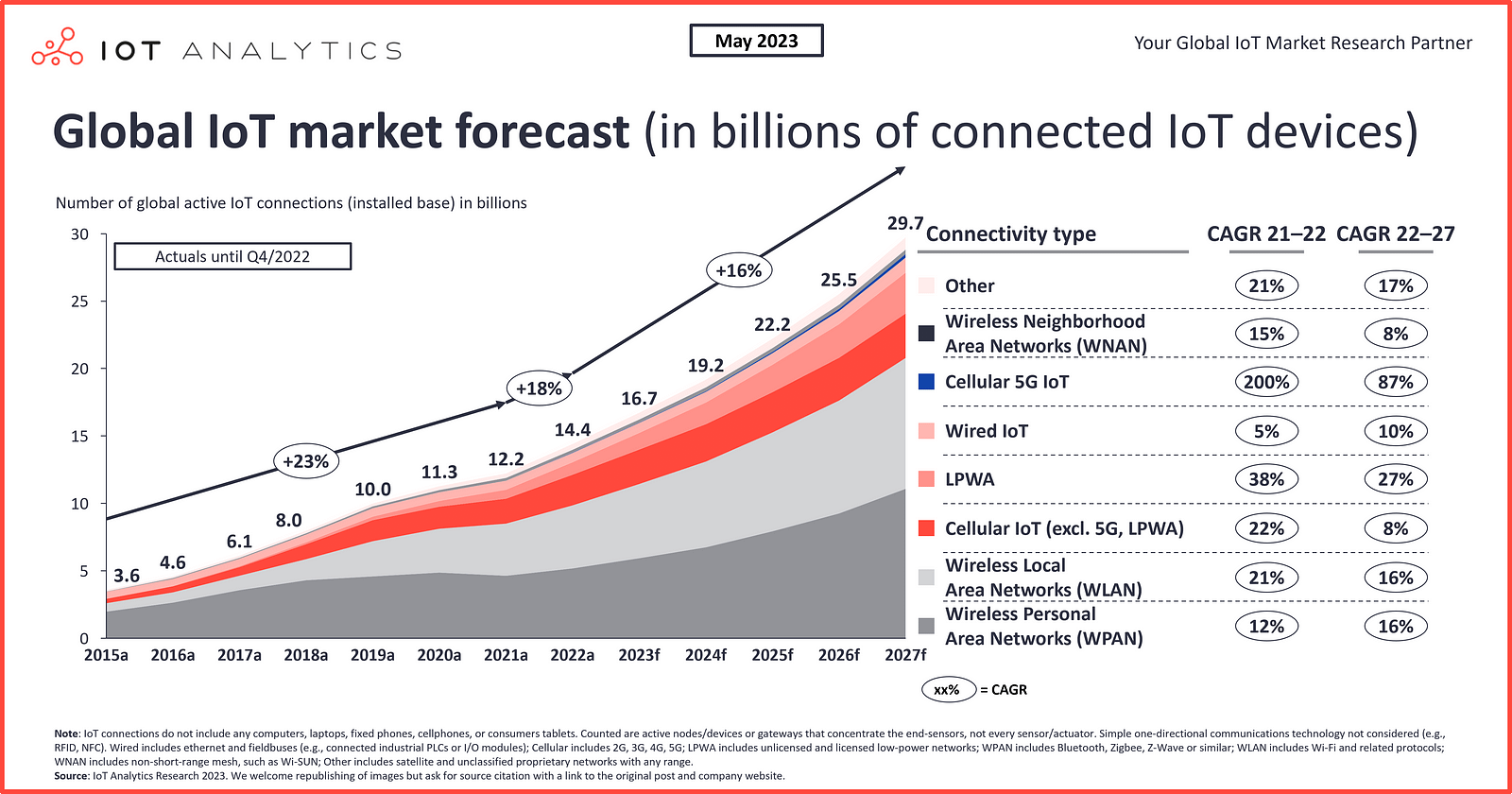
The number of connected devices is soaring at an unprecedented rate. The latest IoT Analytics “State of IoT — Spring 2023” report shows that the number of global IoT connections grew by 18% in 2022 to 14.3 billion active IoT endpoints. In 2023, IoT Analytics expects the global number of connected IoT devices to grow another 16%, to 16.7 billion active endpoints. In this propelling business landscape, embracing IoT is more a necessity than a luxury. IoT helps businesses to optimize operations, enhance customer experiences, and gain a competitive edge in an interconnected world. Thus, by embracing IoT, we can make our environments smarter, more efficient, and more personalized.
In this article, let us try to understand how IoT works, the security aspect and the transformative potential it holds for our future.
How IoT works
As we know, IoT operates through a sophisticated and interdependent network of components, working together seamlessly to deliver its full potential. At its core, there are four basic components — sensors, connectivity, data processing and user interface. The ecosystem functions by collecting data from devices, facilitating data exchange via connectivity, analyzing information, and providing user interfaces for seamless interaction.
Sensors
Sensors are fundamental elements of the IoT ecosystem. These devices are designed to detect and measure specific physical properties such as temperature, humidity, motion, light, or pressure. Sensors can range from simple ones like thermometers to sophisticated ones like cameras or environmental monitors.
- Temperature sensors, enable IoT systems to monitor and regulate the temperature of industrial processes, ensuring optimal conditions and preventing equipment damage.
- Accelerometers detect motion and are utilized in fitness wearables to track physical activity, count steps, and measure acceleration during exercises.
- Light sensors, like photodiodes, enable smart lighting systems to adjust brightness based on natural lighting conditions, reducing energy consumption.
- Proximity sensors, commonly found in automatic doors, detect the presence of individuals and trigger the door to open or close accordingly.
- Gas sensors, such as carbon monoxide detectors, provide early warnings of potentially hazardous gas levels in homes or industrial environments.
Connectivity
Connectivity refers to the ability of IoT devices to connect and interact with each other, as well as with the internet or other network. It is the backbone of IoT, enabling devices to share data within the IoT ecosystem. Various communication technologies facilitate this connectivity, including Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, cellular networks, and even satellite connections.
- Wi-Fi connectivity allows smart home devices, like thermostats or security cameras, to connect to a local network, enabling remote control and monitoring through smartphones or voice assistants.
- Bluetooth connectivity enables seamless pairing between smartphones and wearable devices, like fitness trackers or smartwatches, allowing data synchronization and real-time notifications.
- Cellular networks provide wide-area coverage, allowing IoT applications like asset tracking or fleet management systems to operate across large geographical areas.
- Satellite connectivity enables IoT devices in remote areas, such as environmental monitoring stations in remote forests or maritime vessels, to transmit data to central servers.
Lesser-known connectivity options like LoRaWAN, NB-IoT, Sigfox provide alternatives to the more widely recognized standards. They offer specific advantages in terms of power efficiency, range, cost-effectiveness, and suitability for different IoT use cases.
Data Processing
Data processing is a critical component of the Internet of Things (IoT) ecosystem. It is mainly responsible for analyzing and extracting valuable insights from the massive amounts of data generated by IoT devices. It involves various techniques and algorithms. Data processing in IoT encompasses tasks such as data aggregation, filtering, normalization, and analytics. By applying analytical methods like machine learning and artificial intelligence, data processing enables the identification of patterns and anomalies within the collected data. This, in turn, supports informed decision-making, process optimization, predictive maintenance, and the discovery of new business opportunities across industries ranging from healthcare and manufacturing to transportation and energy.
- In industrial settings, data from sensors embedded in manufacturing equipment are processed in real-time to identify patterns of inefficiency, optimize production processes, and minimize downtime.
- In healthcare, patient monitoring devices gather data on vital signs. It is then processed and analyzed to detect anomalies, trigger alerts, and provide timely medical interventions.
- Environmental sensors deployed in smart agriculture systems collect data on soil moisture, temperature, and humidity. This data is processed to determine optimal irrigation schedules and enhance crop yield.
- In retail, customer behavior data collected through IoT devices can be processed to personalize marketing campaigns, improve inventory management, and enhance the shopping experience.
User Interface
User interfaces provide a means for individuals to interact with and control IoT devices and systems. They allow users to monitor device status, configure settings, receive notifications, and access data insights.
- Mobile applications provide intuitive interfaces for users to control and monitor their smart home devices, and receive notifications or alerts.
- Web-based dashboards offer a centralized platform for businesses to visualize and analyze data collected from various IoT sensors. These dashboards help in enabling real-time monitoring and decision-making.
- Voice-activated assistants, such as Amazon Alexa or Google Assistant, allow users to interact with IoT devices using natural language commands, providing a seamless and hands-free experience.
- Augmented reality (AR) interfaces combined with IoT, can overlay digital information onto the physical environment, enabling interactive and immersive experiences. For example, AR can guide maintenance technicians by overlaying repair instructions onto equipment.

How Safe is IoT?
The rapid proliferation of Internet of Things (IoT) devices has revolutionized various aspects of our lives, offering convenience, efficiency, and automation. However, this rapid expansion has also opened up new vulnerabilities and risks. IoT devices collect and transmit vast amounts of data, often including personal and sensitive information. Inadequate security measures can lead to data breaches, identity theft, or unauthorized surveillance. Additionally, IoT devices are susceptible to exploitation by cybercriminals for launching Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks, using them as entry points to infiltrate networks or hijacking them for malicious purposes.
Security and privacy are critical considerations in IoT. Securing the Internet of Things presents following unique challenges.
- Diversity of Devices, Systems, and Protocols — Implementing uniform security standards is challenging due to the wide range of IoT devices, operating systems, and communication protocols.
- Limitations of Computational Power and Memory— Many IoT devices have constrained resources, making it difficult to implement robust security measures.
- Functionality vs. Security — The rapid pace of IoT innovation often prioritizes functionality over security, resulting in devices with inherent vulnerabilities.
- Long Lifecycle and Patching Challenges — The extended lifespan of IoT devices poses a challenge as security updates may not be regularly provided. This leaves devices exposed to emerging threats.
Evolution of security
With the growing scale of IoT deployments, addressing security challenges becomes increasingly important to maintain trust and protect sensitive information. The IoT security landscape has evolved significantly over the years. As the risks became more apparent, security measures have also undergone rapid development. Measures such as encryption, authentication protocols, and access controls are implemented to safeguard the data and ensure the integrity of the system. Manufacturers are now prioritizing security features during the design and production of IoT devices. Encryption protocols, two-factor authentication, and secure firmware updates are increasingly being implemented to enhance the security of IoT devices. Additionally, advancements in cloud-based security solutions, machine learning, and artificial intelligence are playing a crucial role in detecting and mitigating potential threats in real-time.
The future ahead
The Internet of Things (IoT) has already made significant strides in transforming the way we live and work. As we look ahead, it becomes increasingly clear that the future of IoT is incredibly bright. The potential for innovation, efficiency, and connectivity is vast, promising a world where IoT plays a central role in our daily lives and industries. One of the key factors driving the bright future of IoT is the exponential growth of connected devices. As technology advances, the number of IoT devices continues to soar. By 2030, there will be over 500 billion connected devices worldwide.
IoT’s impact on businesses cannot be overstated. Organizations across industries are realizing the immense potential of IoT to optimize operations, enhance productivity, and drive innovation. With IoT, businesses can collect and analyze vast amounts of data in real-time, enabling them to make data-driven decisions, improve efficiency, and offer personalized experiences to customers.
From transforming industries and businesses to creating smart cities, IoT holds the key to a more connected and intelligent future. By embracing the opportunities presented and addressing challenges, we can shape a future where the potential of IoT is fully realized. The journey has only just begun, and the horizon for IoT looks incredibly promising.
