
How many times did you face a glitch in an electronic device and tried everything you could think of and still did not get it working? You then called up a technician, he came, he checked and he just restarted the device or changed a small setting and voila, the device started working as good as a new one!
We all have been there, at least once in your life ?
Now, consider that you are a CEO of that device company. Imagine how much money you had to spend to fix something so trivial, it might as well be done remotely. Don’t you agree? Well, your thought is basically summing up “device management” in IoT ecosystem
At its core, device management in IoT refers to the processes and tools used to deploy, monitor, update, and maintain IoT devices throughout their lifecycle. This includes activities such as device provisioning, configuration, software updates, security management, diagnostics, and troubleshooting. Effective device management is essential to ensure seamless connectivity, data integrity, and operational efficiency in IoT deployments.
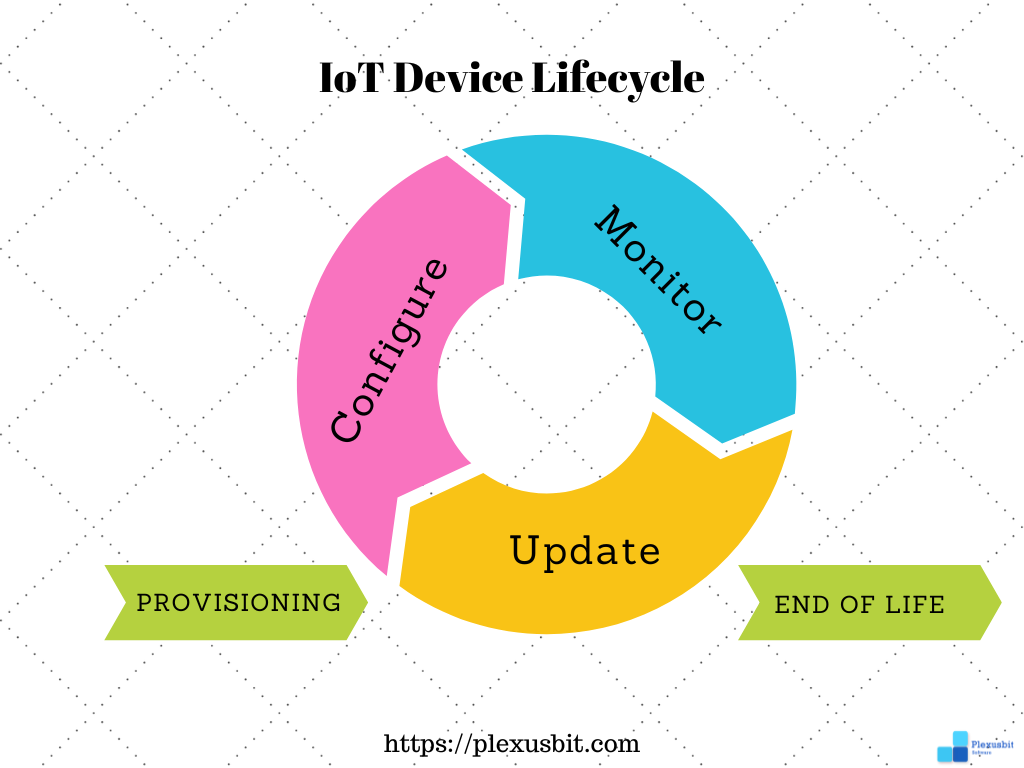
Device Provisioning
This essentially means the initial setup and configuration of IoT devices. This process typically includes tasks such as assigning unique identities, configuring network connectivity, and establishing secure communication channels. Automated provisioning tools and protocols streamline this process, enabling efficient and secure onboarding of large numbers of devices.
Monitoring and Diagnostics
Once devices are provisioned, ongoing monitoring and management become essential. IoT device management platforms provide centralized control and visibility into connected devices, allowing administrators to monitor device health, performance, and connectivity status. Real-time monitoring helps detect and respond to issues promptly, minimizing downtime and optimizing operational efficiency.
Using pattern finding algorithms and continuous improvement in them using feedback loops help administrators to predict demand/usage or even possible failures. IoT is heterogenous and complex in nature. Hence, this is a crucial feature yet mostly not given enough attention for time/cost reasons. It is important to understand that having such a system is an absolute necessity while scaling an IoT business.
Diagnostic tools provide remote access capabilities, enabling administrators to identify and troubleshoot device-specific problems without physical intervention. This reduces maintenance costs, improves uptime, and enhances the overall user experience.
OTA or Remote software updates
Software updates are another compelling aspect of device management in IoT. As the technology landscape evolves, IoT devices need frequent updates to fix bugs, patch vulnerabilities, and add new features. However, updating large numbers of distributed devices manually can be a daunting task. Device management softwares simplify this process by enabling remote software updates, allowing administrators to push updates and patches to many devices simultaneously. An ideal software should also have a retry mechanism considering the fact that IoT mainly depends on networks and they are not available all the time.
Security
Device management also plays a vital role in ensuring the security of IoT deployments. IoT devices are often vulnerable to cyber threats, and a compromised device can have severe consequences. Device management platforms help enforce security policies, apply firmware updates, and manage encryption keys, reducing the risk of unauthorized access and data breaches. Regular security audits and vulnerability assessments can also be performed to identify and mitigate potential risks.
Role of IoT architecture
Device management in the Internet of Things (IoT) may seem like a straightforward task on the surface. But, beneath the apparent simplicity lies a complex web of challenges that can only be overcome with a sturdy IoT architecture as its foundation.
Key points that decide robustness of IoT architecture
Connectivity and communication: An IoT architecture must support various communication protocols and ensure reliable connectivity across different devices, networks, and environments. This ensures seamless data transfer.
Data management and analytics: IoT devices generate vast amounts of data, and effective device management requires the ability to collect, store, analyze, and derive meaningful insights from this data. An IoT architecture should include data management capabilities, such as data ingestion, storage, and processing mechanisms.
Security: Device management plays a crucial role in ensuring the integrity and confidentiality of IoT systems. A robust IoT architecture incorporates security measures at multiple levels, including device authentication, data encryption, access control, and intrusion detection. These security mechanisms protect against unauthorized access, data breaches, and malicious attacks. A strong foundation in security allows device management to enforce security policies, apply firmware updates, and monitor device behaviour for any suspicious activities.
Scalability and flexibility: In IoT deployments, scalability is paramount. As the number of devices grows, the architecture must be able to handle the increasing load without compromising performance or security. A robust IoT architecture incorporates scalable components, such as cloud-based infrastructure, distributed databases, and load balancing mechanisms. This scalability ensures that device management operations can accommodate a growing number of devices and handle the influx of data generated by these devices.
Reliability: IoT deployments often operate in mission-critical environments, where even minor disruptions can have severe consequences. A robust IoT architecture incorporates mechanisms for fault tolerance, redundancy, and disaster recovery. It ensures that device management operations continue uninterrupted, even in the face of failures or network disruptions.

In conclusion, device management plays a pivotal role in the successful implementation and operation of IoT deployments. As IoT technologies continue to evolve, device management platforms and frameworks are adapting to accommodate emerging trends. It is not merely a technical necessity but a strategic imperative for organizations embracing the potential of interconnected devices.
Looking ahead, the future of device management in IoT holds immense promise. As the number of connected devices continues to grow exponentially, there will be a greater need for standardized protocols, seamless interoperability, and scalable architectures. We can expect advancements in edge computing, enabling real-time device management and reducing reliance on centralized cloud infrastructure. Additionally, the rise of 5G networks will unlock new possibilities for device management, providing faster and more reliable connectivity.
By adopting efficient device management practices, businesses can unlock a multitude of benefits.
